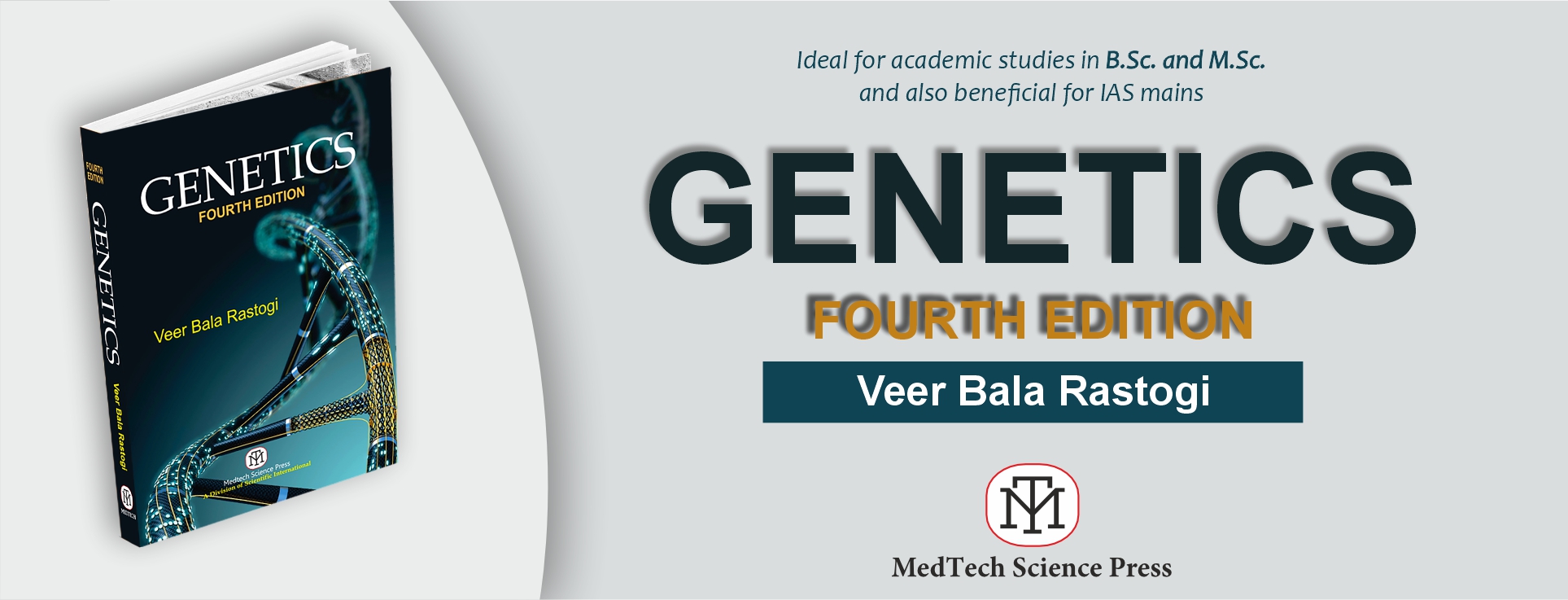
Scientific International is a leading publisher of high-quality academic and scientific books across various fields. Our publications are authored by esteemed experts from India and globally, known for their academic excellence and pedagogical approaches. We publish under the MedTech imprint, a rapidly growing platform covering numerous disciplines. Our mission is to provide cutting-edge, accessible content that inspires curiosity and fosters learning, contributing to the global academic community and supporting students, professionals, and researchers worldwide.
Associated partner

Featured Books
New Arrivals
Top Selling Books
Imprint of Science International





 Continue With Google
Continue With Google
 Continue With Facebook
Continue With Facebook